Knowing how to pop your ears safely is essential for relieving discomfort caused by pressure changes, illness, or congestion. Ear pressure problems are extremely common, especially during air travel, altitude changes, colds, or sinus infections. That blocked, muffled sensation happens when pressure inside your middle ear doesn’t match the external environment.
According to the Mayo Clinic, ear popping helps equalize pressure through the Eustachian tubes, which connect your middle ear to your throat. When these tubes are blocked or slow to adjust, pressure builds up, causing discomfort, hearing changes, or even pain. Learning how to pop your ears correctly can restore balance, improve hearing clarity, and prevent complications.
This comprehensive guide explains exactly how to pop your ears after a flight, when sick, congested, or dealing with a cold. You’ll also learn safe, expert-recommended techniques backed by medical authorities such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Health Service.
Understanding Ear Pressure and Why Your Ears Need to Pop

Ear popping is a natural process that equalizes pressure between your middle ear and the outside environment. This process allows your eardrum to function normally and ensures proper hearing.
When pressure becomes unbalanced, the Eustachian tubes cannot open properly. This leads to a sensation of fullness, muffled hearing, or discomfort. Learning how to pop your ears helps restore this balance safely and naturally.
Key Causes of Ear Pressure Problems
• Air Travel and Altitude Changes
During airplane takeoff and landing, cabin pressure changes rapidly. Your middle ear must adjust to match external pressure. If adjustment doesn’t happen quickly, pressure builds up, causing discomfort. Learning how to pop your ears after a flight helps relieve this imbalance quickly. This is why frequent flyers often use pressure-equalizing techniques during descent.
• Sinus Congestion and Inflammation
Congestion blocks the Eustachian tubes, preventing air movement. This blockage causes pressure buildup and muffled hearing. Understanding how to pop your ears when congested helps reopen blocked pathways. Clearing congestion allows normal pressure equalization.
• Colds and Respiratory Infections
Illness increases mucus production and inflammation. This restricts airflow through ear pressure channels. Knowing how to pop your ears with a cold helps restore normal ear function. Proper techniques reduce discomfort and improve hearing clarity.
• Allergies and Seasonal Irritation
Allergic reactions cause swelling inside nasal passages. This interferes with pressure balance mechanisms. Learning how to pop your ears when sick is especially helpful during allergy season.
• Scuba Diving and Water Pressure Changes
Water pressure increases rapidly underwater. Equalizing pressure is essential to prevent injury. Proper ear popping techniques protect the eardrum.
• Rapid Elevation Changes During Travel
Mountain driving or elevator rides can also affect ear pressure. Equalization techniques prevent discomfort.
Also Read:- How to Carve a Turkey: The Complete Step-by-Step Expert Guide
How the Ear Equalizes Pressure Naturally
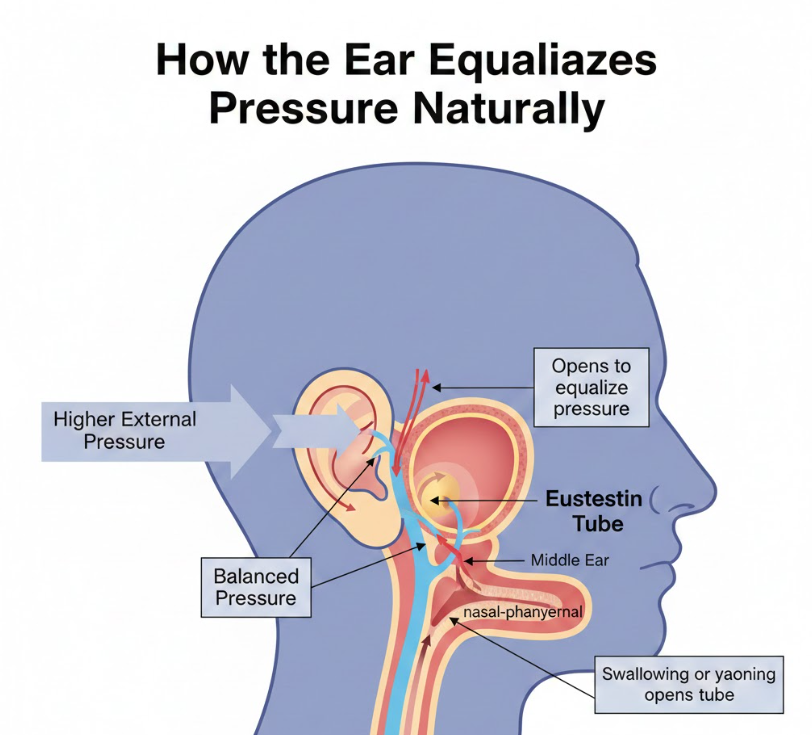
Your ears contain a small canal called the Eustachian tube. This tube opens and closes to balance pressure automatically.
When working properly, swallowing, yawning, or chewing activates these tubes. These actions allow air to move freely between your throat and middle ear. This explains why simple movements help when learning how to pop your ears.
Natural Ear Pressure Equalization Mechanisms
• Swallowing Activates Ear Pressure Control
Swallowing triggers muscle movements that open the Eustachian tubes. This allows air to flow and equalize pressure. Frequent swallowing helps relieve ear pressure during flights.
• Yawning Creates Natural Pressure Release
Yawning stretches muscles connected to ear pressure control. This encourages tubes to open naturally.
• Chewing Stimulates Ear Muscles
Chewing gum or food activates muscles around the ear canal. This improves pressure balance.
• Jaw Movement Improves Airflow
Moving your jaw forward or side-to-side opens pressure channels.
• Breathing Techniques Support Equalization
Controlled breathing helps regulate internal pressure.
• Body Position Affects Ear Pressure Balance
Sitting upright improves airflow and pressure equalization.
Also Read:- How to Sell Pokémon Cards: The Complete Expert Guide to Maximizing Value
How to Pop Your Ears Safely : Proven Techniques

There are several medically recommended ways to equalize ear pressure safely.
Safe and Effective Ear Popping Methods
• Swallowing Frequently
Swallowing is the safest and easiest way to equalize ear pressure. It activates muscles that open the Eustachian tubes. Drinking water or sucking on candy encourages swallowing. This method works well for mild pressure changes.
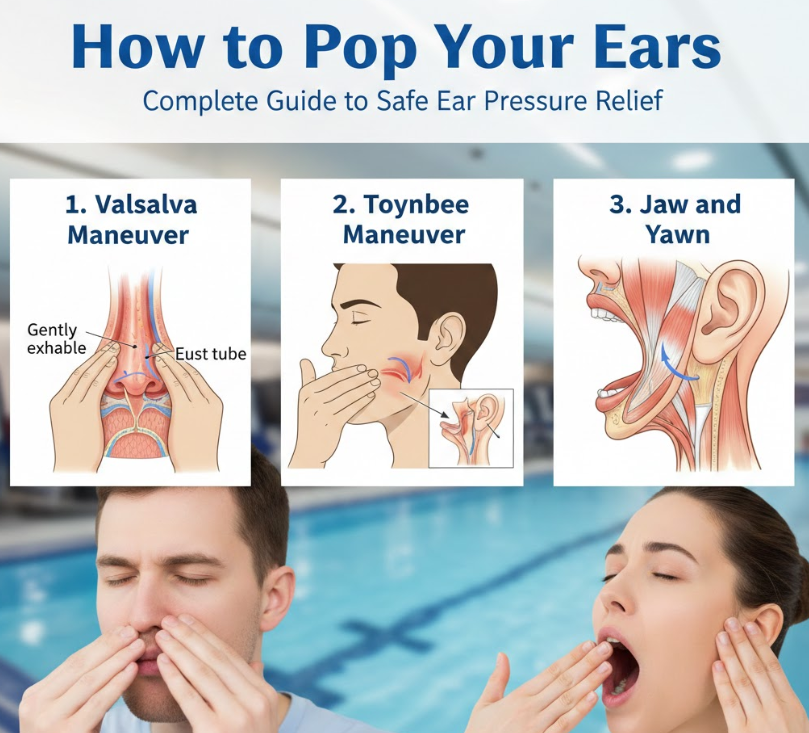
• Yawning to Open Ear Canals
Yawning stretches ear-connected muscles. This allows pressure to equalize naturally. Even forced yawning can help.
• Valsalva Maneuver Technique
Close your mouth, pinch your nose, and gently blow. This forces air into pressure tubes. This is one of the most effective ways to learn how to pop your ears safely.
• Chewing Gum or Eating Food
Chewing activates pressure-regulating muscles. This is especially useful during flights.
• Toynbee Maneuver Method
Pinch your nose and swallow simultaneously. This helps equalize pressure quickly.
• Steam Inhalation Therapy
Warm steam reduces congestion and improves airflow.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery recommends gentle pressure equalization methods rather than forceful techniques.
Also Read:- How to Sell Gold: The Complete Expert Guide to Getting the Best Value
How to Pop Your Ears After a Flight

Air travel is the most common cause of ear pressure problems. Cabin pressure changes rapidly during takeoff and landing.
Understanding how to pop your ears after a flight prevents discomfort and improves hearing quickly.
Best Techniques After Air Travel
• Swallow and Drink Water Immediately
Drinking water stimulates swallowing. This activates pressure equalization mechanisms. Frequent swallowing helps restore balance after flights.
• Use the Valsalva Maneuver Carefully
Pinch your nose and gently blow. This forces air through blocked tubes. Avoid excessive force.
• Chew Gum or Eat Food
Chewing activates ear muscles. This improves airflow and relieves pressure.
• Walk Around and Move Your Jaw
Movement improves circulation and muscle activation.
• Apply Warm Compresses to Ears
Heat improves blood flow and reduces blockage.
• Use Nasal Decongestants if Needed
Decongestants reduce swelling and improve airflow.
The World Health Organization recommends managing congestion before flights to reduce ear pressure risk.
Also Read:- How to Store Peaches: The Complete Expert Guide to Keeping Peaches Fresh Longer
How to Pop Your Ears When Sick

Illness makes ear popping more difficult due to inflammation and mucus buildup.
Learning how to pop your ears when sick requires treating the underlying condition.
Best Techniques During Illness
• Stay Hydrated to Thin Mucus
Water helps reduce congestion. Thinner mucus improves airflow.
• Use Steam Therapy Regularly
Steam reduces inflammation and clears blockages.
• Use Saline Nasal Sprays
Saline clears nasal passages safely.
• Rest and Allow Recovery
Healing reduces inflammation naturally.
• Use Gentle Pressure Techniques Only
Avoid forceful pressure equalization.
• Seek Medical Help if Symptoms Persist
Persistent blockage may indicate infection.
Also Read:- How to Make a Paper Airplane: The Ultimate Step-by-Step Guide for Distance, Speed, and Fun
How to Pop Your Ears When Congested

Congestion blocks airflow and pressure equalization pathways.
Knowing how to pop your ears when congested helps restore hearing clarity and comfort.
Congestion Relief Methods
• Steam Inhalation Therapy
Steam loosens mucus and improves airflow.
• Use Humidifiers to Improve Air Moisture
Moist air reduces inflammation.
• Stay Hydrated Throughout the Day
Hydration improves mucus flow.
• Use Gentle Equalization Techniques
Avoid aggressive pressure.
• Use Over-the-Counter Decongestants Carefully
Follow medical advice.
• Practice Breathing Exercises
Controlled breathing improves pressure balance.
When NOT to Pop Your Ears
Avoid ear popping if:
• Severe ear pain exists
• Ear infection is present
• Recent ear surgery occurred
• Hearing loss is sudden
Consult medical professionals if symptoms persist.
Also Read:- How to Cut a Mango: The Complete Step-by-Step Guide for Perfect Slices and Cubes
Conclusion: Mastering How to Pop Your Ears Safely
Understanding how to pop your ears helps relieve discomfort, restore hearing clarity, and prevent complications. Whether caused by flights, illness, congestion, or colds, proper pressure equalization techniques provide safe and effective relief.
Using expert-recommended methods such as swallowing, yawning, steam inhalation, and gentle pressure techniques ensures safe results. Avoid aggressive force and seek medical help if symptoms persist.
With the right knowledge and safe practices, you can confidently manage ear pressure and maintain optimal ear health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for ears to pop naturally?
Usually within minutes to hours, depending on the cause.
Is it safe to force ear popping?
Gentle methods are safe. Avoid excessive force.
Why won’t my ears pop after flying?
Congestion or inflammation may block pressure equalization.
Can ear popping damage hearing?
Improper force can cause injury. Use gentle methods.
When should I see a doctor?
If symptoms last longer than a few days.
For More Updates Visit: Biomagazine







Leave a Reply